E' un blog personale dove Francesco Paganelli inserisce dei commenti, considerazioni e osservazioni che riguardano: esperienze vissute, ricerche e studi compiuti, attualità.
6 marzo 2015
How to create a tar file encrypted with gpg in linux
22 febbraio 2015
How to delete files when minimum free space is reached
Below I have reported a script, find out in a forum page.
This can be scheduled and it will delete file in a folder when free disk space reaches a threshold:
#!/bin/bash
# Immediately exit upon shell error
set -e
# Set lock file details
scriptname=$(basename $0)
lock="/var/run/${scriptname}"
# Lock the process, or exit if already running
exec 200>$lock
flock -n 200 || exit 1
# Write the PID to the lock file
pid=$$
echo $pid 1>&200
# Define the location of the applications
DF="/bin/df"
AWK="/usr/bin/awk"
SED="/bin/sed"
FIND="/usr/bin/find"
# Define the directory to check
DIR="/motion"
# Define constants
Minimum=100 # Minimum space below which files will be deleted (MB)
DeleteTo=200 # Delete files until this value is reached (MB)
NumtoDel=100 # Number of files to delete between each free disk space check
# Set shell such that empty file listing will return null
shopt -s nullglob
# Check if free space is less than the minimum specified
FreeSpace=$($DF -m $DIR | $AWK '{print $4}' | $SED "1d")
if [ $FreeSpace -lt $Minimum ]; then
# Free space has dropped below minimum value, delete files until DeleteTo space is free
while [ $FreeSpace -lt $DeleteTo ]; do
# Check if any pictures remain in the directory, otherwise break out of the delete loop
if test -z "$($FIND $DIR -maxdepth 1 -name '*.jpg' -print -quit)"; then
break
fi
# Delete files until NumtoDel has been reached, or no more files exist
FileCount=0;
for FileName in $DIR/*.jpg; do
rm $FileName
FileCount=$((FileCount+1))
# Check if number of files to delete has been reached
if [ $FileCount -ge $NumtoDel ]; then
break
fi
done
# Check if free space is less than the minimum specified
FreeSpace=$($DF -m $DIR | $AWK '{print $4}' | sed "1d")
done
fi
8 febbraio 2015
How create a Xiaopan OS VM in Virtualbox
Xiaopan OS is an easy to use security and penetration testing with a collection of wireless security and forensics tools. It includes a number of advanced tools for network administrators, security professionals and home users to test the strength of their wireless networks and eliminate any vulnerabilities.
In the next step we will see how create a VM with the Xiaopan OS.
1. Open VirtualBox and click on the button "New". In the popup insert the name of the new VM, select "Linux" as Type and "Other Linux" as Version. After that click "Next".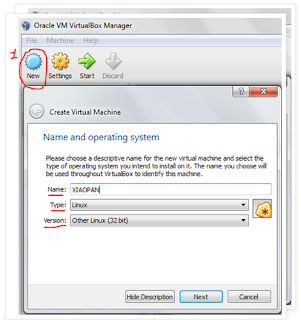
2. In the next popup you have to choose the memory size, you can to assign 512MB to the your new VM. Then click “Next”.
3. Now it’s necessary create a new virtual hard drive. Then click “Create”.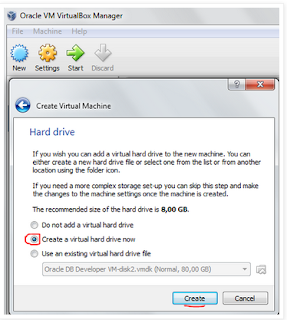
4. The new hard driver can be a VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image). Then click “Next”.
5. Leave the default option “Dynamically allocated”, in order to avoid to allocate immediately all the space. Then click “Next”.
6. It’s sufficient assign only 2 GB at the new VM. Then click “Next”.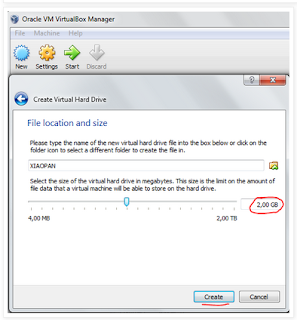
7. Now, it’s necessary download the ISO image from the “Sourceforge” portal: http://sourceforge.net/projects/xiaopanos/
8. After download the iso image, you have to assign it to the vm. In the VM settings, in the “Storage” section, select the cd-rom disk image, browse the file system (click on the cd-rom) and select the iso image file.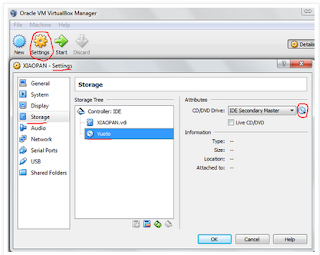
9. At the end you can start the virtual machine, during the boot you must select “Boot XIAOPAN OS in Virtualization”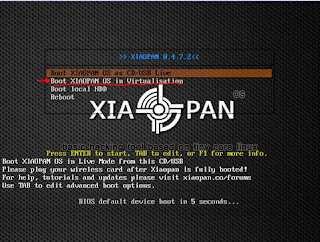
Enjoy it!
Bye